Time,
like an ever-rolling stream keeps moving. Technology advances. Civilization brings more and more rules. Every tragedy from the Titanic to the Herald
of Free Enterprise to the recent sinking of the Costa Concordia demonstrates
one thing that does not change – human nature has its weaknesses. Technology, to an extent, can produce the best
of missiles but the man behind the launching mechanism retains the control and
continues to be relevant. Better
educated, exposed and aware, perhaps, but still vulnerable to human frailties. When organizations adopt the system approach,
they set in place an atmosphere of continual improvement.
“A
bad system will defeat a good person every time” – W. Edwards Deming. This reminds me of a quote from the Cain
Mutiny, which in essence says, “Navy is a master plan devised by the genius for
execution by idiots”. This master plan
is the system, which should be so created that there is no need to blame the
individual. Every time the system fails,
the management reviews and acts to work on the procedures that comprise the
system. Improve the system enabling
better protection of the individual.
It is
ironic that individuals who are assigned the designing and then implementing of
the system often consider it a burden – little realizing that the system
approach takes management away from asking, “Who” to asking, “How and Why”. This results in further development of the
system rather than blaming the individual who was simply working within the
system.
In
the maritime world, the P&I clubs may well be paying the insurance dues
only after an individual is blamed, but the ISM Code in contradiction does not
encourage the blame culture. Good
management personnel understand this. Both
the ISM Code and the process-based management system standard, ISO 9001, take
management away from the blame culture and require continual improvement of the
system.
Management,
which can connect the clauses 4, 5, 8 and 9 of the ISM Code will understand and
appreciate the fundamentals of the Code.
These members of management will reap dividends in terms of “cash in the
bank”. The term, “cash in the bank”,
coined by QMII over 25 years ago, implies fewer to no accidents, resulting in
greater customer satisfaction and an increase to the bottom line. In the maritime world, the difference between
a detention and a catastrophe really is the cost the company pays – the loss in
revenue, the cash in the bank lost. It
implies loss of life, which in bare terms costs the organization. Loss of a vessel can ruin the company.
If it
is as simple as the correct implementation of the process-based approach, then
why does management not get it? Is it
because the maritime industry is so drowned in day-to-day activities that it is
more concerned with avoiding being detained, somehow getting away from Port
State Control (PSC) scrutiny, to be unable to implement the ISM Code in the
real sense? Alternatively, is it that
the old-fashioned top management (after all, those who go into management are a
generation or two behind those who actually go to sea and operate the vessels)
are not fully exposed to the true meaning of the system approach?
This analysis
is not new. Justice Sheen investigating
the loss of the Herald of Free Enterprise found a “disease of sloppiness” and negligence
at every level of the corporate hierarchy. What did that mean? It meant the system was not working. In present-day man-made tragedies, we, too,
conclude the system is not working.
Shore
management and those at sea should already know the value of a correctly
implemented process-based management system (ISM Code in conjunction with ISO
9001:2008). The implementation of the Safety
Management System (SMS) to prevent detention is not acceptable. It should be one of the benefits of a good
system. Aligning the system to just meet auditor requirements or take measures
to prevent PSC actions is weakening the system. The system will do that, however, the system
should have a more honest, larger purpose where it welcomes nonconformities (NC)to enable management (both at sea and ashore) to fulfill their obligations
under the ISM Code (clause 9). Correction
of NCs, followed by Root Cause Analysis does not end the cycle.
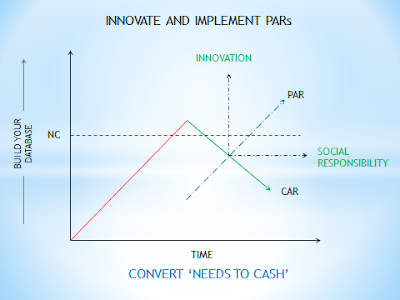
I
have drawn this graph above to show the benefits of respecting NCs (CARs). As
the data base builds information can be obtained from the data to objectively
analyze it and get the trends and predict potential NCs. When a system is first
implemented, the number of NCs will increase. This is because the system is now
recording the deficiencies. As the data base builds the analytical ability of
the system is able to get the desired information for the managements to
resource the system (be it in hardware, equipment, training or manpower) and
most importantly to recognize potential NCs. This then positively affects the
bottom line as now we are tackling potential NC and not being reactive to NCs.
There is a point in the system development of an organization where the NCs
drop and the PARs (Preventive Action Requests) increase indicative of the
employees having matured and embraced the system. This is the place where the
management also sees innovative ideas coming up and the management taking a
more socially responsible role.
Preventing
detention too often becomes the Master’s primary responsibility to the shore
based management. For PSC activities not
to reveal NCs is a daily short-term goal. Actually, this is counterproductive to the
expectation of the Code and the system approach in general. It encourages “hood winking” the PSC officers.
In my experience at sea and in my
interaction with seafarers I have come across incidents of seafarers being paid
‘bonuses’ to get a clean audit report. If management takes that path, true
safety cannot be achieved. The PSC
officers are stakeholders in maritime safety at sea. Why have the PSC officers come in? They meet a public outcry and demand following
the numerous tragedies over the years. They
detain vessels in order to prevent disaster at sea from occurring. What would the management prefer – a catastrophe
or a detention? Which is less expensive?
In
the selection of Top Management (TM) at sea, be it the Captain, the Chief
Engineer or the Hotel Captain (on passenger vessels from the Titanic to Costa Concordia)
– if the Master does not perform or does not conduct him-self professionally or
as per expectations, whose fault is it? Management ultimately picks the crews. The hiring procedure needs to be targeted. Those at sea are performing to the best of
their abilities and working hard; it is their profession and life. We must never forget that they are performing
as per the selection criteria that management has set! Often for seafarers the relationship with the
vessel is from ‘gangway to gangway’. How does a company go about ensuring that
its seafarers are equally invested in the success of the system? Some say that
retention of seafarers is the answer. But is a high retention percentage
indicative of a good ISM culture? The answer again lies in a better management
system. The Culture should filter top
down. The blaming of individuals should shift to blaming the system in order to
encourage a more open system. There
should be no fear in exposing NCs.
The
only bad nonconformity is the one we do not know about. A system should be created which welcomes nonconformities. A detention is a NC, which has saved an
organization from a likely catastrophe. Detentions
are expensive; therefore, the need to create an SMS in the true spirit so it
ensures NCs are detected internally, well in time, enabling management to take
corrective action to determine the root cause. To do that after each mishap, management
should not jump to the CHECK stage of the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle.
They
should instead go back to the ACT stage and carry out better management reviews,
leading to better planning followed by correct implementation (DO) of the
system. The system approach, correctly
implemented, will lead to a system, which will work. Moreover, when the system works, one of the
many benefits will be few to no detentions. The ISM Code is the basis for such a system. An investment in a correctly designed system
and the implementation together with active participation by management will
ensure requirements are met. When
requirements are met, there will not be any detentions. Let us not prepare for audits,
detentions and PSC exams. That principle
is incorrect. Let management encourage
those at sea, and those who manage the vessels from shore, (as the
Superintendents, Port Captains, DPs and CSOs, etc.) to work together in the
interest of a system which functions and leads to safety at sea.
The
sinking of the Costa Concordia has brought into focus several SMS-related
failures, from which timely and correct lessons must be learned to prevent the
recurrence of similar catastrophic events.
These accidents will shape industry’s culture and motivate industry
stakeholders to make vessel operations safer in an effort to continue to
sustain the shipping business and ultimately create “cash in the bank”.
The
ISM Code recognizes that human error is the cause of the majority of
accidents. The Code requires delineating
responsibilities of the ship and shore side management, creating the system and
then addressing the coordination of the ship-to-shore support. If about eighty percent of marine incidents
are caused by human error, companies then have the responsibility to create true
organizational management systems, which help humans, prevent and mitigate such
incidents. The management system is
documented to the extent necessary for effective planning, prevention, operation
and control. The most important parts of
any management system are not documented as they involve leadership, care and
coordination.
The fish-bone diagram above indicates the principled working of a system. The inputs are worked on using the system to produce the desired output. The passengers coming
on board will need the entire work spectrum indicated in the fish-bone diagram
to work together under the Top Management exercising care and coordination for
the output to be positive. For the satisfied passengers, to continue to
patronize the company because, their expectations have been met in terms of the
holiday, safety, and security and pollution prevention.
The fish bone diagram above has the vital rib – Care and Coordination – implying active
and constant participation of the top management. The PDCA cycle at the Act
stage (please see diagram above) requires the TM to act based on the review of
the system. Audits are not meant to deliver changes or improve the system. If
audits and auditors could improve a system, then auditors would be the CEOs of
the shipping companies! It is the management that improves their systems. For this,
they must understand their systems and lead the implementation of the system by
example. To do this, management must
admit they also need to be trained.
The
correct implementation of the SMS, based on the ISM Code, will ensure that
ships operate safely. The Code addresses
the key provisions such as SMS objectives, safety and environmental protection policy,
company responsibility and authority, designated person, master’s responsibility
and authority, resources and personnel, shipboard operations, emergency preparedness,
reports and analysis of nonconformities, accidents and hazardous occurrences, maintenance
of the ship and equipment, documentation, company verification, and review and
evaluation. All of the provisions of the
Code are designed to work interactively and in harmony with each other to
enable the management system to be effective.
However, none of this can deliver the desired results without the total
involvement and commitment of the company’s top management. Blaming individuals
will only correct one person and not the system. To improve the system, the root cause should
be considered. The management must take
the blame for having a poor hiring process and lead the change by re-designing that
process. When the Captain at sea fails
in his role, management must read it as the process having failed, not having
been designed correctly. It requires
going back to the PLAN stage of the PDCA cycle.
One
of the main risks that any shipping company encounters is the potential
disconnect that can occur when the procedures in the SMS are not being followed
by shore side personnel, seagoing officers and crew. The worst that can happen to a company is
when those ashore believe that the procedures are being followed, when in
actuality, due to, for example, over documentation or lack of awareness and
training, they are not. Seafarers in our
courses share experiences of over-documentation in certain companies where the
‘paper’ eventually takes more importance that the actual procedure. This
disconnect again is indicative of a system not functioning. It is indicative of a cookie cutter system
based on generic templates (a common culture in the maritime industry). The designing of a system must be based on the
“As-Is” or current state. If consultants
are used to assist in designing the system, beware of those who promise to do
it cheaply sitting in their offices and providing master solutions! If you accept these, then as TM you have
already sown the seed of a weed. Do not
expect it to give you roses! Good
investment at the PLAN stage of the PDCA cycle is vital, in terms of both money
and time. Investment in designing the
correct system based on the existing state is vital to the success of the
system.
Any
major marine incident investigation, like the Costa Concordia, should focus on
the ability of a company to effectively implement their SMS procedures and
whether or not there were any gaps in how the SMS procedures were applied.
If a
company believes it has a perfect system and rests on its laurels, it is doomed
to failure.



No comments:
Post a Comment